Air circulation is one of the most important factors for a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. Whether it’s a home, office, warehouse or industrial site, proper ventilation helps control temperature, remove pollutants, reduce humidity and maintain fresh air. But one of the most common questions people ask is: “How much ventilation does my room actually need?”
The answer lies in CFM airflow. CFM or Cubic Feet per Minute is the standard measurement to calculate how much air needs to be exchanged in a room per minute. Getting this calculation right is critical for your ventilation system to be efficient.
This article will guide you through everything you need to know about CFM airflow, including how to calculate it, common mistakes to avoid and why solutions like Shutter Exhaust Fans are ideal for commercial and industrial applications..
What is CFM and Why It Matters
CFM stands for cubic feet per minute, it measures the volume of air flowing through a specific point in one minute. It’s the foundation of every successful HVAC system design and the heartbeat of ventilation systems. Just as blood circulation is vital to human health, proper airflow is essential to a building’s respiratory system.
It indicates the amount of air a fan is capable of moving. For example a fan rated at 500 CFM can move 500 cubic feet of air every minute. This measurement helps you match a ventilation system to the actual size and needs of your space.
Why airflow measurement is important for ventilation
Accurate airflow measurement has a direct impact on several aspects of indoor environments. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, the average American spends 90% of their time indoors where air quality is typically two to five times worse than outdoor air. This makes proper ventilation not just a comfort issue but a health necessity.
Inadequate airflow measurement can lead to serious consequences:
- Air quality degradation: Insufficient airflow causes stagnant air, odor buildup and pollutant accumulation
- Energy inefficiency: Oversized systems waste energy while undersized ones work harder than necessary
- Comfort inconsistencies: Improper airflow creates hot and cold spots throughout spaces
- Equipment damage: Incorrect sizing leads to premature system wear and failures
Also indoor air pollution is estimated to cost $75 billion annually in lost productivity making proper ventilation an economic consideration as well.
Why Getting the Right CFM is Important
Proper airflow balance is a critical factor in creating healthy and efficient indoor environments. The consequences of incorrect CFM calculations go beyond just discomfort.
1) Air quality and comfort
Proper CFM ensures air reaches every part of a home evenly, eliminating hot and cold spots that plague poorly ventilated spaces. Since indoor air is two to five times more polluted than outdoor air, calibrated airflow is essential in removing contaminants. Poor ventilation is responsible for nearly half of all indoor air quality issues in nonindustrial workplaces. Prolonged exposure to poor ventilation can trigger respiratory issues, allergies and even occupational asthma.
2) Energy efficiency and system performance
CFM rates directly impact operational costs. Systems that move air at the right rate use less energy to maintain desired temperatures. Improper sizing leads to short cycling or excessive runtime, wasting energy and increasing utility bills. Energy recovery ventilation systems can recover 70-80% of energy in existing air, ultimately reducing costs by 10-15% or more.
3) Risks of over- or under-ventilation
Oversized systems push excessive air, leading to inconsistent temperatures and faster equipment deterioration. Undersized systems struggle to meet comfort requirements, overworking components and shortening their lifespan. Under-ventilation allows pollutants to accumulate, causing headaches, dizziness and fatigue. Excess humidity from poor ventilation leads to mold growth and structural damage.
How to Calculate CFM for Each Room or Space.
The precise equation for CFM calculations varies depending on the type of space and the conditions it must meet. The basic equation for all room types is: CFM = Room Volume × ACH ÷ 60.
Living rooms and bedrooms.
Living rooms and bedrooms usually need 6-8 ACH. For typical rooms with 8-foot ceilings, the general guideline is to allow 1–2 CFM for each square foot of space. A 300 square foot bedroom that needs two air changes per hour would be approximately 80 CFM.
Bathrooms and kitchens
Bathrooms require higher ventilation rates, typically 8-10 ACH, for effective moisture control. Small bathrooms under 100 square feet need a minimum of 50 CFM, larger bathrooms require additional capacity for fixtures: +50 CFM for each toilet or shower, and +100 CFM for jetted tubs.
Kitchens require the highest residential ventilation at 15-20 ACH for odor and grease removal. Range hoods should provide 100 CFM per linear foot against a wall or 150 CFM per foot for island installations.
Grow tents and greenhouses
For growth spaces the volume equals the base CFM requirement. However accessories add to the needed airflow. Carbon filters add 60%, ducting adds 20% and grow lights add up to 50% more CFM.
Attics and whole-house systems
Whole house fans should provide airflow equal to at least half the home’s volume. For attic ventilation multiply the square footage by 0.7 for minimum CFM requirements. For high quality exhaust fans that ventilate your spaces check out shutter exhaust fans.
Recommended CFM by Room Type
Here’s a quick guide to airflow requirements for different spaces:
| Room Type | Air Changes per Hour (ACH) | Example CFM Requirement |
| Bedrooms | 5–6 ACH | 100–150 CFM |
| Living Rooms | 6 ACH | 150–250 CFM |
| Kitchens | 15–20 ACH | 300–500 CFM |
| Bathrooms | 8–12 ACH | 80–150 CFM |
| Basements | 10–12 ACH | 200–400 CFM |
| Warehouses/Workshops | 6–10 ACH | 1000+ CFM |
| Commercial Spaces | 8–12 ACH | 500–1500 CFM |
This table shows why one-size-fits-all solutions don’t work. A bathroom needs quick air turnover to prevent moisture, a large warehouse needs heavy-duty solutions like shutter exhaust fans or high-CFM inline systems.
Common Mistakes in Ventilation Sizing
Even with a CFM calculator mistakes are common. Here are some of the biggest mistakes to avoid:
- Undersizing the fan. Too little airflow means poor ventilation and rising humidity.
- Oversizing the fan. More isn’t always better, oversized fans can waste energy, create noise and even cause drafts.
- Ignoring duct resistance. Bends, filters and long ducts reduce airflow efficiency.
- Forgetting commercial requirements. Warehouses, restaurants and industrial spaces need much higher airflow than homes.
Best Ventilation Solutions for Different Spaces
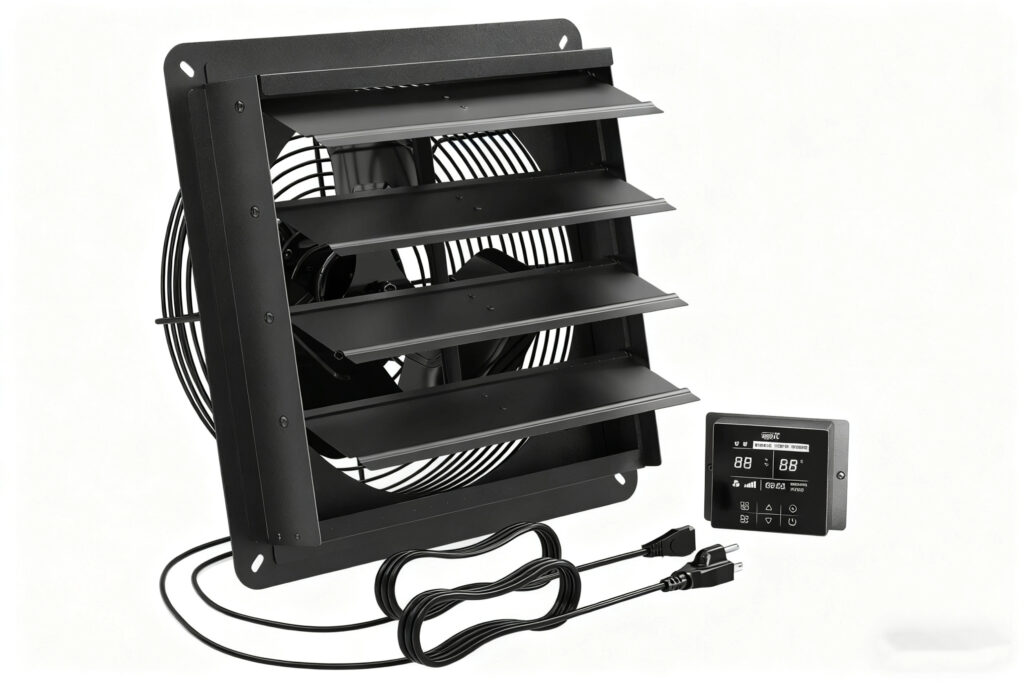

Now that you know how to calculate airflow, the next step is to choose the right equipment.
Shutter Exhaust Fans
These are perfect for warehouses, garages and workshops. They allow high volumes of air to move efficiently and prevent backflow when not in use. See options here: Shutter Exhaust Fans.
Inline Fan Systems
Great for ducted applications where noise reduction and consistent airflow are priorities. Common in commercial kitchens and HVAC setups.
830 CFM Ventilation Fan
Ideal for medium-to-large rooms where a precise high-output fan is needed. Reliable for commercial applications where constant airflow is required.
By choosing the right type of fan you ensure your calculated CFM translates into real-world performance.
Factors That Affect Your CFM Needs
Various factors influence the amount of airflow a space requires making precise calculations essential for effective ventilation systems.
1) Room size and ceiling height
Calculating cubic footage forms the foundation of accurate CFM determination. Larger rooms need higher airflow rates to maintain air quality. To measure this, multiply the length, width and height of the room to get its volume. Rooms with high or vaulted ceilings alter the way air moves, so they often need more ventilation than standard rooms.
2) Air change rate (ACH) requirements
Different spaces require different air change rates based on their function:
- Bedrooms and living rooms: 5-6 ACH and 6-8 ACH, respectively
- Kitchens: 7-8 ACH for residential and up to 15-20 ACH for commercial
- Bathrooms: 7-8 ACH to control moisture
- Attics with air conditioning: 12-15 ACH
The Centers for Disease Control recommends aiming for at least 5 ACH of clean air to help reduce airborne contaminants.
3. Filters, Ducting and Fans
Air filters, ducts and fans all reduce airflow. For example, a filter may reduce airflow by 15-20%. Long ducts or sharp bends also cut down CFM performance. A good filter should handle about 2.5 CFM per square inch. If the filter is too small it clogs quickly and reduces airflow.
4. Heat from Lights or Appliances
Heat producing items increase airflow needs. In kitchens, grilling or frying creates extra heat and smoke so you need more ventilation. In greenhouses or grow rooms strong lights and equipment can increase CFM needs by up to 50%.
Why Aitecac Ventilation Solutions Stand Out
When it comes to ventilation you don’t just want any fan. You want the right system for your specific needs. Aitecac delivers solutions designed for industrial, commercial, and heavy-duty applications.
Here’s why customers trust Aitecac:
- High quality materials: designed for durability and long term use.
- Advanced design: Shutter Exhaust Fans ensure efficient airflow and energy savings.
- Wide application range: for homes, businesses, warehouses and factories.
- Customer focused solutions: designed to solve real world ventilation problems.
With Aitecac, you get more than just a fan, you get reliable air management that protects health, comfort and efficiency.
Conclusion: Get the Right Ventilation Today
Ventilation is not optional. It’s essential for comfort, health and efficiency. Using a CFM airflow calculator, you can easily determine the airflow requirements for any room. Once you know the number, choosing the right fan becomes simple. Instead of trial and error, invest in proven solutions. Shutter Exhaust Fans are powerful, efficient and built for demanding spaces.
Don’t wait until poor air quality becomes a problem. Explore our range of shutter exhaust fans today and get the airflow your room needs.





